Each search engine has its own process for building a search index. Below is a simplified version of the process Google uses.
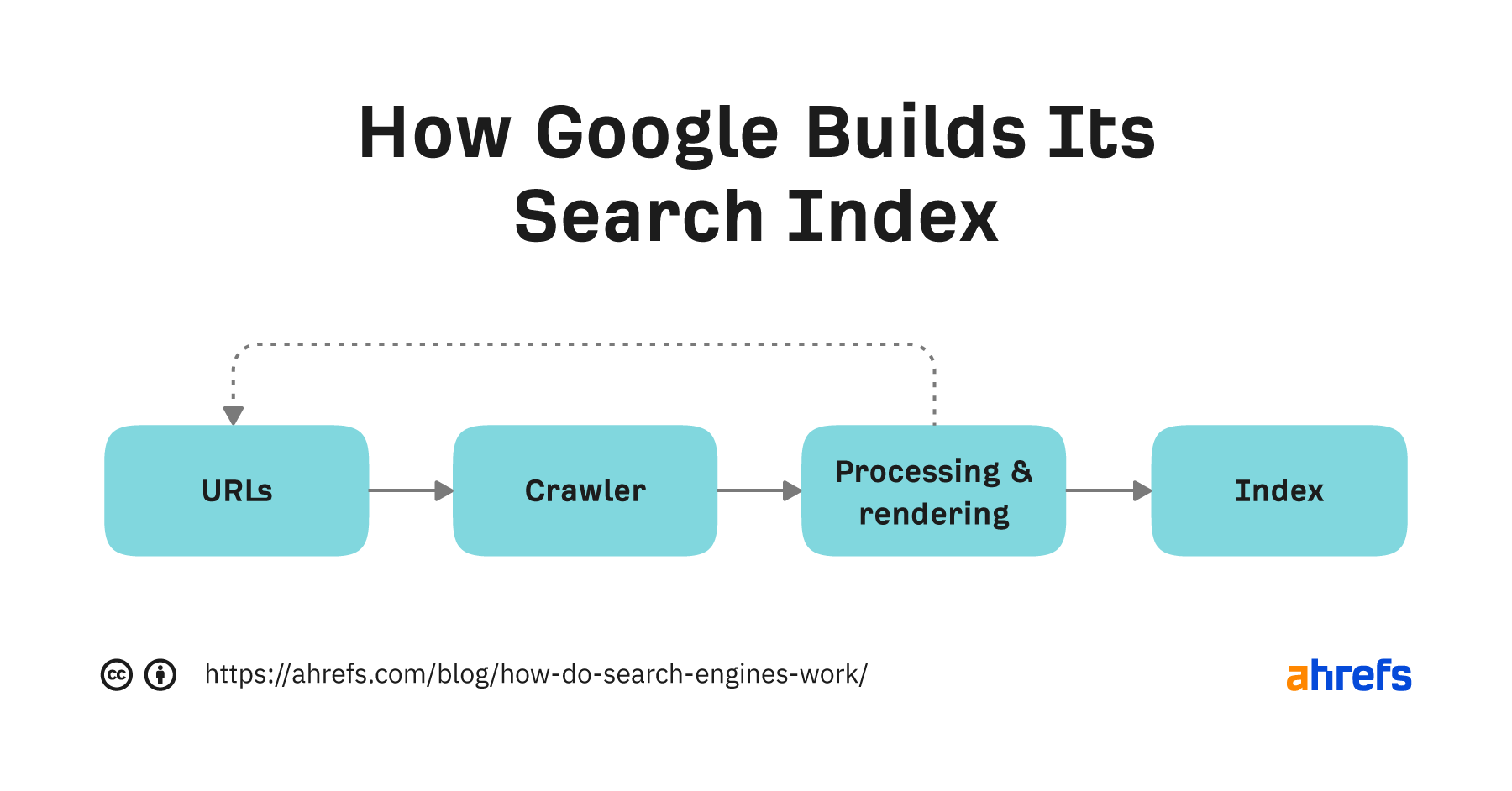
Let’s break it down.
URLs
Everything begins with a known list of URLs. Google discovers these in many ways, but the three most common are:
- From backlinks. Google has an index of hundreds of billions of webpages. If someone links to a new page from a known page, Google can find it from there.
- From sitemaps. Sitemaps tell Google which pages and files you think are important on your site.
- From URL submissions. Google lets site owners request crawling of individual URLs in Google Search Console.
Crawling
Crawling is where a computer bot called a spider visits and downloads known URLs. Google’s crawler is Googlebot.
Processing and rendering
Processing is where Google works to understand and extract key information from crawled pages. To do this, it has to render the page, which is where it runs the page’s code to understand how it looks for users.
Nobody outside of Google knows every detail about this process. But it doesn’t matter. All we really need to know is that it involves extracting links and storing content for indexing.
Indexing
Indexing is where processed information from crawled pages gets added to the search index.
The search index is what you search when you use a search engine. That’s why getting indexed in major search engines like Google and Bing is so important. Users can’t find you unless you’re in the index.
Leave a Reply